AAU universities conduct a majority of the federally funded university research that contributes to our economic competitiveness, health and well-being, and national security. AAU universities are growing our economy through invention and innovation while preparing the next generation of scientists and engineers for global leadership. By moving research into the marketplace AAU universities are helping to create jobs, and provide society with new medicines and technologies.
A study by researchers at Duke University School of Medicine found that supplying healthy mitochrondra to damaged nerve cells can signifantly help millions managing pain from diabetic neuropathy and chemotherapy.

Researchers from the USF College of Marine Science are studying soft tissue samples from barnacles, oysters, and fish to better understand the state of contamination and its origins in Tampa Bay, Florida's largest estuary.
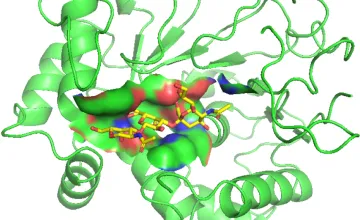
The advancement lays the groundwork for creating a library of sugar-recognizing proteins that may help detect and treat diverse illnesses.

The olfactory senses of ants help them hunt, detect outsiders, and know their role within a colony. In a new study, researchers have discovered how ants can switch one gene on out of hundreds to ensure their survival.
Explore More: University Research
You can filter stories by the university.
New research from Rice University and the Ohio State University indicates that mindless switching between digital devices is associated with increased susceptibility to food temptations and lack of self-control, which may result in weight gain.
University of Rochester research shows how sleep depth can impact our brain’s ability to efficiently wash away waste and toxic proteins.
Research completed by two University of Arizona medical students shows a tragic trend in overdose-related, out-of-hospital cardiac arrests in Arizona.
University of California, Berkeley scientists inserted a gene for a green-light receptor into the eyes of blind mice and, a month later, the mice were navigating around obstacles as easily as those with no vision problems.
Research from the Georgia Institute of Technology shows an ultra-low power hybrid chip that gets inspiration from the brain could help give palm-sized robots the ability to collaborate and learn from their experiences, researchers report.
