AAU universities conduct a majority of the federally funded university research that contributes to our economic competitiveness, health and well-being, and national security. AAU universities are growing our economy through invention and innovation while preparing the next generation of scientists and engineers for global leadership. By moving research into the marketplace AAU universities are helping to create jobs, and provide society with new medicines and technologies.
A study by researchers at Duke University School of Medicine found that supplying healthy mitochrondra to damaged nerve cells can signifantly help millions managing pain from diabetic neuropathy and chemotherapy.

Researchers from the USF College of Marine Science are studying soft tissue samples from barnacles, oysters, and fish to better understand the state of contamination and its origins in Tampa Bay, Florida's largest estuary.
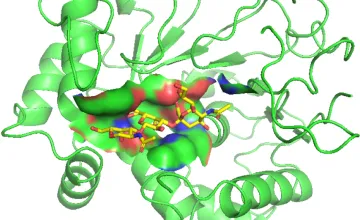
The advancement lays the groundwork for creating a library of sugar-recognizing proteins that may help detect and treat diverse illnesses.

The olfactory senses of ants help them hunt, detect outsiders, and know their role within a colony. In a new study, researchers have discovered how ants can switch one gene on out of hundreds to ensure their survival.
Explore More: University Research
You can filter stories by the university.
Surface mapping technology such as GPS, radar and laser scanning have long been used to measure features on the Earth’s surface. Now, a new computational technique developed at The University of Texas at Austin is allowing scientists to use those technologies to look inside the planet.
A new MIT study shows that a cognitive strategy focused on social good may help people cope with distressing events.
An exoplanet infamous for its deadly weather has been hiding another bizarre feature—it reeks of rotten eggs, according to a new Johns Hopkins University study of data from the James Webb Space Telescope.
New research from the University of Utah demonstrates how wind-carried dust from the exposed bed of Great Salt Lake is disproportionately affecting disadvantaged communities in the Salt Lake metro area.
A new way to store carbon captured from the atmosphere developed by researchers at The University of Texas at Austin works much faster than current methods without the harmful chemical accelerants they require.
