AAU universities conduct a majority of the federally funded university research that contributes to our economic competitiveness, health and well-being, and national security. AAU universities are growing our economy through invention and innovation while preparing the next generation of scientists and engineers for global leadership. By moving research into the marketplace AAU universities are helping to create jobs, and provide society with new medicines and technologies.
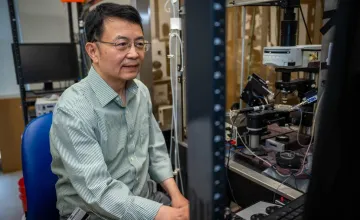
A study by researchers at Duke University School of Medicine found that supplying healthy mitochrondra to damaged nerve cells can signifantly help millions managing pain from diabetic neuropathy and chemotherapy.

Researchers from the USF College of Marine Science are studying soft tissue samples from barnacles, oysters, and fish to better understand the state of contamination and its origins in Tampa Bay, Florida's largest estuary.
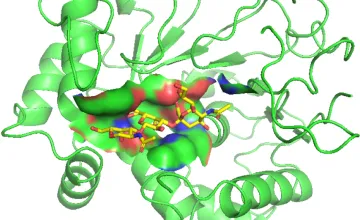
The advancement lays the groundwork for creating a library of sugar-recognizing proteins that may help detect and treat diverse illnesses.

The olfactory senses of ants help them hunt, detect outsiders, and know their role within a colony. In a new study, researchers have discovered how ants can switch one gene on out of hundreds to ensure their survival.
Explore More: University Research
You can filter stories by the university.
Chemical transformation of human glial cells into neurons
A five-year, $4.2 million grant from the National Science Foundation will empower researchers from multiple institutions in the U.S. and Mongolia to develop wide-ranging scientific knowledge of river systems spanning two continents. KU is the lead institution for the project.
New research from the Texas A&M Health Science Center College of Medicine hints that post-traumatic epilepsy (PTE) might be tied to the body’s own immune response.
A University of Virginia engineering professor is exploring ways to improve polymer membranes to make desalination simpler and less expensive.
Princeton University use mathematical equations to show that physiological differences between trees and grasses explain the curious phenomenon of heavy rainfalls and spells of drought on the African savannas created significantly fewer trees.
