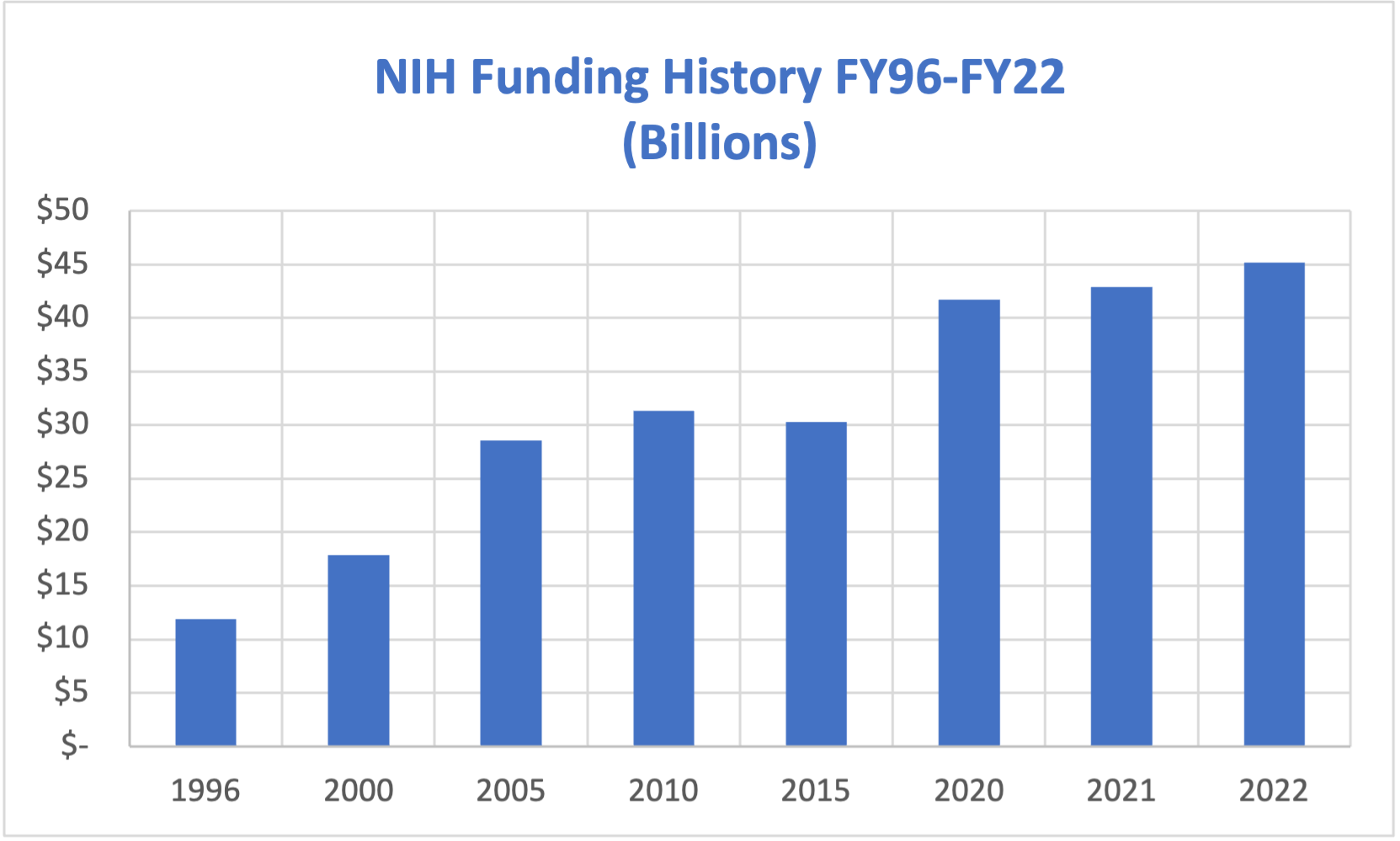
AAU urges Congress to provide at least $49 billion for the National Institutes of Health in FY23.
This increased investment would allow for the NIH’s base budget to keep pace with the biomedical research and development price index (BRDPI) and allow meaningful investment growth of 5%. This level of investment represents sustained, predictable growth and allows the United States to invest in scientific opportunities. NIH research enhances public health, lengthens life, and reduces illness and disability. America’s investments in NIH research yielded huge advances in responding to COVID-19. Strong platforms and a skilled workforce jumpstarted COVID-19 diagnostics, vaccines, and treatments. NIH-funded research in vaccine development helped identify a new way to respond to viruses through novel mRNA vaccines.
AAU supports the intent of President Biden’s proposed ARPA-H initiative under the umbrella of the NIH. Any funds appropriated for this new initiative should supplement, not supplant, the critical functions of NIH’s basic research led by a rigorous peer review system.
NIH research enhances public health, lengthens life, and reduces illness and disability. NIH contributes to American economic growth and productivity, and expands biomedical knowledge by funding cutting-edge research and cultivating the biomedical workforce of today and tomorrow.
NIH contributes to American economic growth and productivity and expands biomedical knowledge by funding cutting-edge research and cultivating the biomedical workforce of today and tomorrow. Keeping NIH on a pathway to restoring its purchasing power after a decade of loss to inflation and budget cuts is critical to sustaining our extraordinary progress in human health over the past several decades. Continued investment in biotechnology and genomics has proven crucial to understanding complex disease pathologies. Improved understanding of the molecular causes of disease is being used to screen thousands of chemicals for potential drug candidates and search for ways to prevent disease.